HKDSE 2024 Maths Paper II 題解
HKDSE 2024 Maths Paper II Answers and Solutions
香港中學文憑考試 2024 數學卷二答案+題解,括號內數字為答對百分率。
因版權關係,無法在網上刊登試題。請自行購買,或到公共圖書館借閱。
資料來源:香港考試及評核局─考試報告及試題專輯
&\ (x +3y)^2 -(x -3y)^2\\
=&\ \big((x+3y) +(x -3y)\big)\big((x+3y) -(x -3y)\big)\\
=&\ (2x)(6y)\\
=&\ 12xy
\end{align*}$$
方法二:
&\ (x +3y)^2 -(x -3y)^2\\
=&\ (x^2 +6xy +9y^2) -(x^2 -6xy +9y^2)\\
=&\ x^2 +6xy +9y^2 -x^2 +6xy -9y^2\\
=&\ 12xy
\end{align*}$$
&\ \frac{(2\alpha)^3}{(4\alpha^{-5})^{-1}}\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{8\alpha^3}{4^{-1}\alpha^5}\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{4 \times 8\alpha^3}{\alpha^5}\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{32}{\alpha^2}
\end{align*}$$
k &= \frac{5}{2m} +n\\[2pt] k -n &= \frac{5}{2m}\\[2pt] m &= \frac{5}{2(k -n)}
\end{align*}$$
A 是正確。以下列出各選項的正確近似值。
C. 18.2 (correct to 3 significant figures 三位有效數字)
D. 18.2483 (correct to 4 decimal places 四位小數)
C. 18.2 (cor. to 3 sig. fig. 三位有效數字)
D. 18.2483 (cor. to 4 d.p. 四位小數)
Let the price of an apple and a lemon be x and y respectively.
$$\begin{cases}
2x +3y = 38\\
3x + 2y = 47
\end{cases}$$
解聯立方程
Solving the equations,
$$x = 13, y=4$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ 4x + 7y\\
=&\ 4(13) +7(4)\\
=&\ $80
\end{align*}$$
4x^2 +2ax +3a &\equiv x(4x +b) +2c\\
4x^2 \color{red}{+2ax} \color{blue}{+3a} &\equiv 4x^2 \color{red}{+bx} \color{blue}{+2c}
\end{align*}$$
比較係數
Comparing the coefficients,
$$\begin{align*}
2a &= b\\
\frac{a}{b} &= \frac{1}{2}\\
a:b &= 1:2\\[6pt]
3a &=2c\\
\frac{a}{c} &= \frac{2}{3}\\
a:c &= 2:3
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}
a &: &b &\ &= 1 &: &2 &\ \\
a &\ &\ &:c &= 2 &\ &\ &:3 \\
\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}
a &: &b &\ &= 2 &: &4 &\ \\
a &\ &\ &:c &= 2 &\ &\ &:3 \\
\hline{}
a &: &b &: c &= 2 &: &4 &:3 \\
\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{align*}
x^2 -3x &= (m -1)^2 -3(m -1)\\
x^2 -(m -1)^2 &= 3x -3(m -1)\\
\big(x +(m -1)\big)\big(x -(m -1)\big) &= 3x -3m +3\\
(x +m -1)(x -m +1) &= 3(x -m +1)\\
(x +m -1)\color{red}{(x -m +1)} -3\color{red}{(x -m +1)} &= 0\\
\color{red}{(x -m +1)}(x +m -1 -3) &= 0\\
(x -m +1)(x +m -4) &= 0\\
x -m +1 = 0\ \ \text{or}\ \ x +m -4 &= 0\\
x = m -1\ \ \text{or}\ \ x &= 4 -m
\end{align*}$$
方法二:
把各選項中的解代入方程,如果左方和右方相等,該解為正確。
$$\begin{align*}
x^2 -3x &= (m -1)^2 -3(m -1)\\
x^2 -3x &= m^2 -2m +1 -3m +3\\
x^2 -3x &= m^2 -5m +4
\end{align*}$$
當 x = m − 1,
$$\begin{align*}
\text{LHS 左方} &= (m -1)^2 -3(m -1)\\
&= m^2 -2m +1 -3m +3\\
&= m^2 -5m +4\\
&=\text{RHS 右方}
\end{align*}$$
因此 x = m − 1 為方程的解,並可排除選項 C 及 D。
當 x = m − 4,
$$\begin{align*}
\text{LHS 左方} &= (m -4)^2 -3(m -4)\\
&= m^2 -8m +16 -3m +12\\
&= m^2 -11m +28\\
&\neq\text{RHS 右方}
\end{align*}$$
因此 x = m − 4 並不是方程的解,亦可排除選項 A。
當 x = 4 − m,
$$\begin{align*}
\text{LHS 左方} &= (4 -m)^2 -3(4 -m)\\
&= 16 -8m +m^2 -12 +3m\\
&= m^2 -5m +4\\
&=\text{RHS 右方}
\end{align*}$$
因此 x = 4 − m 為方程的解,所以答案為 B
g(1) &= g(2)\\
(1 +1)(1 +a) &= (2 +1)(2 +a)\\
2(1 +a) &= 3(2+a)\\
2 +2a &= 6 +3a\\
2 -6 &= 3a -2a\\
a &= -4\\[8pt] \end{align*}$$
$$ \therefore g(x) = (x +1)(x -4)\\[10pt]
\begin{align*}
g(a) &= g(-4)\\
&= (-4 +1)(-4 -4)\\
&= (-3)(-8)\\
&= 24
\end{align*}$$
f(x) is divisible by x + k.
∴ f(−k)=0
$$\begin{align*}
f(-k) &= 0\\
(-k)^3 +k(-k)^2 +5(-k) +10 &= 0\\
-k^3 +k^3 -5k +10 &= 0\\
k &= 2
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ \text{remainder 餘式}\\
=&\ f(-1)\\
=&\ (-1)^3 +2(-1)^2 +5(-1) + 10\\
=&\ -1 +2 -5 +10\\
=&\ 6
\end{align*}$$
\begin{align*}
\frac{1 -x}{2} &\ge 4 & \text{or}&\ & 7 +5x &\le -3\\
1 -x &\ge 8 & \text{or}&\ & 5x &\le -10\\
-x &\ge 7 & \text{or}&\ & x &\le -2\\
x &\le -7 & \text{or}&\ & x &\le -2\\
\end{align*}\\
\ \\
\therefore x \le -2$$
Let the total number of students be N.
$$\begin{align*}
N \times 40\% &= N \times 40\% \times \beta \% + N \times 60\% \times 30\%\\
0.4 &= 0.4 \times \beta \% +0.18\\
0.22 &= 0.4 \times \beta \%\\
0.22 \div 0.4 &= \beta \%\\
\beta \% &= 0.55\\
\beta \% &= 55\%
\end{align*}$$
$$\text{平均速率}= \frac{\text{總行走距離}}{\text{總花費時間}}\\[2pt] \text{Average Speed}= \frac{\text{Total distance travelled}}{\text{Total Time Spent}}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ \text{總行走距離 Total distance travelled}\\
=&\ 60 \times \frac{18}{60} +40 \times \frac{27}{60}\\[2pt]
=&\ 36\,\text{km}
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
&\ \text{平均速率 Average speed}\\[2pt]
=&\ \frac{36\,\text{km}}{\frac{18+27}{60}\text{h}}\\[2pt]
=&\ 48\,\text{km/h}
\end{align*}$$
\text{Let 設}\ z &=\frac{kx^2}{y}\\
\end{align*}$$
z的新值 New Value of z
=&\ \frac{k[(1 +20\%)x]^2}{(1 -20\%)y}\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{1.2^2}{0.8} \times\frac{kx^2}{y}\\[2pt] =&\ 1.8z
\end{align*}$$
百份數變化 Percentage Change
=&\ \frac{1.8z-z}{z}\times 100\%\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{0.8z}{z}\times 100\%\\[2pt] =&\ 80\%
\end{align*}$$
相關文章: 變分與百分數變化 Variation and Percentage Change
y &= 2(6 -x)^2 -7\\
&= 2(36 -12x +x^2) -7\\
&= 72 -24x +2x^2 -7\\
&= 2x^2 -24x +65
\end{align*}$$
A)
##x^2## 的係數為正數,即是圖像開口向上。
The coefficient of ##x^2## is positive. Thus, the graph opens upwards.
因此選項 A 為正確答案。
B)
當 ##y=0##,
$$\begin{align*}
2x^2 -24x +65 &= 0\\
x=4.13\ \text{or}\ x&=7.87
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 B 錯誤。
C)
## y = 2x^2 -24x +65##
所以 y-截距 y-intercept = 65。
因此選項 C 錯誤。
D)
當 ##x=-6##
$$\begin{align*}
y &= 2\big(6-(-6)\big)^2 -7\\
&= 281\\
&\neq -7
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 D 錯誤。
2 \pi r \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg} = 8\pi\ ..(1)\\
\pi r^2 \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg} = 80\pi\ ..(2)
\end{cases}$$ $$
(2) \div (1)\\
\begin{align*}
\frac{\pi r^2 \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg}}{2 \pi r \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg}} &= \frac{80\pi}{8\pi}\\[2pt] \frac{r}{2} &= 10\\[2pt] r &= 20
\end{align*}$$
把 ##r=20## 代入 (1)
2 \pi (20) \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg} &= 8\pi\\[2pt] 40 \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg} &= 8\\[2pt] \theta &= 72\deg
\end{align*}$$
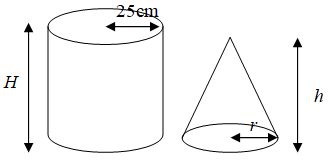
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{H}{h} &= \frac{32}{15}\\[12pt]
\frac{\pi(25)^2H}{\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2h} &= \frac{10}{9}\\[2pt]
\frac{25^2H}{\frac{1}{3}r^2h} &= \frac{10}{9}\\[2pt]
\frac{625H}{r^2h} &= \frac{10}{9} \times \frac{1}{3}\\[2pt]
\frac{625}{r^2} \times \frac{32}{15} &= \frac{10}{27}\ \Big(\because\frac{H}{h} = \frac{32}{15}\Big)\\[2pt]
\frac{1}{r^2} &= \frac{1}{3600}\\[2pt]
r^2 &= 3600\\[2pt]
r &= 60\,\text{cm}
\end{align*}$$
由於 AMFE 是平行四邊形,所以 ##AE = MF##,因此 ##CF=k##。
let ##AE=3k, ED=k, BM=MC=2k##.
Since AMFE is a parallelogram, ##AE = MF##. Thus, ##CF=k##.

1) 證明 Prove DG = GC
留意 △GDE ≅ △GCF (AAS),
因此 DG = GC = 2k

2) 求 △BFG面積
留意 △BMH ~ △BFG (AAA)

設 △BFG面積為 x。
Let the area of △BFG be x.
\frac{4}{x} &= \Big(\frac{2k}{2k +2k +k}\Big)^2\\[2pt] \frac{4}{x} &= \Big(\frac{2k}{5k}\Big)^2\\[2pt] \frac{4}{x} &= \frac{4}{25}\\[2pt] x &= 25
\end{align*}$$
3) 求 k
從 △BFG面積求 k的值。
Find the value of k from the area of △BFG.

$$\begin{align*}
\frac{(2k+2k+k)(2k)}{2} &= 25\\[2pt]
\frac{(5k)(2k)}{2} &= 25\\[2pt]
5k^2 &= 25\\[2pt]
k^2 &= 5\\
k &= \sqrt{5}
\end{align*}$$
4) 求 AEGH 面積

$$\begin{align*}
&\ AEGH\text{ 面積}\\
=&\ (4k)^2 -\color{blue}{\frac{(2k)(k)}{2}} -\color{green}{\frac{(4k)(2k)}{2}} -\color{red}{\frac{(2k)(4k)}{2}} +4\\[2pt]
=&\ 16k^2 -\color{blue}{k^2} -\color{green}{4k^2} -\color{red}{4k^2} +4\\
=&\ 7k^2 +4\\
=&\ 7(5) +4\ \ (\because k^2=5)\\
=&\ 39\,\text{cm}^2
\end{align*}$$
Note that ∠ABD is a right angle.
證明 Proof:
BC^2 +BD^2 &= 5^2 +12^3\\
&= 25+144\\
&= 169\\
&= 13^2\\
&= CD^2
\end{align*}$$
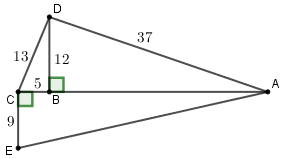 $$
$$
\begin{align*}
AB^2 +BD^2 &= AD^2\\
AB^2 +12^2 &= 37^2\\
AB &= 35
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
AC^2 + CE^2 &= AE^2\\
(5+35)^2 + 9^2 &= AE^2\\
AE &= 41
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
&\ \text{周界 Perimeter}\\
=&\ 37 +13 +9 +41\\
=&\ 100\,\text{cm}
\end{align*}$$
Refer to the figure, construct two parallel lines.
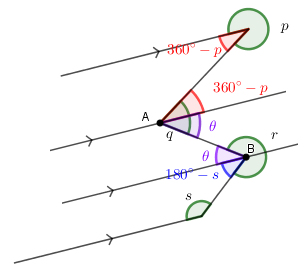
在 B 點,
\color{purple}{\theta} &= 360\deg -\color{green}{r} -\color{blue}{(180\deg -s)}\\
&= 360\deg -r -180\deg +s\\
&= 180\deg -r +s
\end{align*}$$
在 A 點,
q &= \color{red}{(360\deg -p)} +\color{purple}{\theta}\\
q &= 360\deg -p +180\deg -r +s\\
p +q +r -s &= 540\deg
\end{align*}$$
Let n be the number of side of the polygon.
$$\begin{align*}
(n -2)\times 180\deg &= 900\deg\\
n -2 &= 5\\
n &= 7
\end{align*}$$
I)
對角線數目 Number of Diagonals ##= C_2^7 -7=14##,所以選項 I 錯誤。

II)
Number of folds 折數 = 邊數 = 7,所以選項 II 正確。
III)
Number of axes 對稱軸數目 = 邊數 = 7,所以選項 III 正確。
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇 #7 多邊形性質
A rhombus is a parallelogram with four equal sides. The figure below shows its properties.

I)
∵∠DEC = ∠FCG = 90°
∴DE//FC

下圖所示的5隻角大小相同。
The 5 angles shown below are the same.

∠EDI = ∠ICF (alt. ∠s 錯角, DE//FC)
∠ADE = ∠DEI (alt. ∠s 錯角, AD//EI)
∠DEI = ∠IFC (alt. ∠s 錯角, DE//FC) ∵∠IFC = ∠ICF
∴CI = FI
因此選項 I 正確。
II)

設 ∠ABE = x,
得到 ∠EBC = x, ∠BCE = 90° − x
∴∠GCH = 90° − x, ∠ABE = x
因此選項 II 並非必然正確。
III)
參考下圖,

∠CHF = ∠HCG (alt. ∠s 錯角, FH//CG)
∴∠DAE = ∠CHF = 90° − x ∠DEA = ∠CFH = 90°
下一步是證明 DE = FC

∠DEC = ∠FCE = 90°
EC = CE (Common side 公共邊)
∴△DEC ≅ △FCE (AAS) DE = FC
∴△ADE ≅ △HCF (AAS)
因此選項 III 正確。
Both AC and BE are diameters of the circle. So, their intersection is the centre of the circle.
設圓心為 O點。
Let the centre be point O.

∵OA = OB
∴∠OAB = ∠OBA = 46°
$$\begin{align*}
\color{red}{\angle POB} &= \color{green}{\angle OAB} +\color{green}{\angle OBA}\ \text{(Ext}\ \angle\ \text{of}\ \triangle\ \text{外角})\\
&= 46\deg +46\deg\\
&= 92\deg
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
\color{purple}{\angle APD} &= \color{red}{\angle POB} +\color{blue}{\angle PBO}\ \text{(Ext}\ \angle\ \text{of}\ \triangle\ \text{外角})\\
&= 92\deg +16\deg\\
&= 108\deg
\end{align*}$$
\tan \phi &= \frac{CD}{BC}\\[2pt] BC &= \frac{CD}{\tan \phi}\\[10pt] \sin \theta &= \frac{CD}{AD}\\[2pt] AD &= \frac{CD}{\sin \theta}
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
\frac{BC}{AD} &= \frac{\frac{CD}{\tan \phi}}{\frac{CD}{\sin \theta}}\\[2pt] &= \frac{CD}{\tan \phi} \times \frac{\sin \theta}{CD}\\[2pt] &= \frac{\sin \theta}{\tan \phi}
\end{align*}$$

$$U=(-3,-8)\\
V=(8,-3)\\
W=(-4,-3)$$
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇 #5 坐標旋轉 Rotation of Coordinates
設 P = (h, k)
把 (h, k) 代入 x − y + 13 = 0
Put (h, k) into x − y + 13 = 0
$$\begin{align*}
h -k +13 &= 0\\
h = k -13
\end{align*}\\
\ \\
\therefore P = (k -13,k)$$ $$\begin{align*}
AP &= PB\\
\sqrt{(k -13 +3)^2 + (k -1)^2} &= \sqrt{(k -13 +7)^2 + (k +5)^2}\\
(k -10)^2 + (k -1)^2 &= (k -6)^2 + (k +5)^2\\
k^2 -20k +100 +k^2 -2k +1 &= k^2 -12k +36 +k^2 +10k +25\\
-22k +101 &= -2k +61\\
40 &= 20k\\
k &= 2
\end{align*}$$
方法二:
由於 AP = PB,因此 P點在 AB 的垂直平分線上。
Since AP = PB, point P lies on the perpendicular bisector of AB.
設 M 點為 AB 的中點。
Let point M be the mid-point of AB.
$$\begin{align*} M&=\Big(\frac{-3 -7}{2},\frac{1 -5}{2}\Big)=(-5,-2)\\[8pt]
m_{AB} &= \frac{1 +5}{-3 +7}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{6}{4}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{3}{2}
\end{align*}$$
設 m 為垂直平分線的斜率。
Let m be the slope of the perpendicular bisector.
$$\begin{align*}
m \times m_{AB} & = -1\\[2pt]
m \times \frac{3}{2} &= -1\\
m &= \frac{-2}{3}
\end{align*}$$
y +2 &= \frac{-2}{3}(x +5)\\[2pt] 3y +6 &= -2x -10\\
2x +3y +16 &= 0
\end{align*}$$
解以下聯立方程 Solving the equations
$$\begin{cases}
2x +3y +16 =0\\
x -y +13 =0
\end{cases}\\
\ \\
P=(-11, 2)$$

If two straight lines do not intersect, they must be parallel.
$$\begin{cases}
6x -8y = 7k\\
kx +12y = 5
\end{cases}\\
\begin{cases}
y = \frac{3}{4}x – \frac{7k}{8}\\
y = \frac{-k}{12}x +\frac{5}{12}
\end{cases}$$
它們的斜率相等
Their slopes are equal.
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{3}{4} &= \frac{-k}{12}\\[2pt]
36 &= -4k\\
k &= -9
\end{align*}$$
3x^2 +3y^2 -6x +12y -4 &= 0\\
x^2 +y^2 -2x +4y -\frac{4}{3} &= 0
\end{align*}$$ $$
\text{圓心 Centre}=(1, -2)\\
\begin{align*}
\text{半徑 radius} &= \sqrt{1^2 +2^2 +\frac{4}{3}}\\[2pt] &= \sqrt{\frac{19}{3}}\\
&\approx 2.52
\end{align*}$$
I)
方法一:
把 (0, 0) 代入圓形方程
Put (0, 0) into the equation of circle
&\ 3(0)^2 +3(0)^2 -6(0) +12(0) -4\\
=&\ -4\\
\lt&\ 0
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 I 正確。
方法二:
原點與圓心的距離
The distance between the origin and centre
&\ \sqrt{(1 -0)^2 +(-2 -0)^2}\\
=&\ \sqrt{5}\\
=&\ 2.24\\
\lt&\ 2.52
\end{align*}$$
該距離小於半徑,因此原點在圓形之內。
The distance is shorter than the length of radius. Thus, the origin lies inside the circle.
因此選項 I 正確。
II)
$$\begin{align*}
\text{圓周 Circumference} &= 2\pi(2.52)\\
&\approx 15.8\\
&\lt 16
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 II 正確。
III)
參考下圖,

該距離 ##= 0-(-2) = 2##
因此選項 III 正確。
Number of Possible Combinations ##=C_2^6 = 15##
列出所有積不小於 12 的組合
List out all combinations whose products are not less than 12.
{2, 6}
{3, 4}
{3, 5}
{3, 6}
{4, 5}
{4, 6}
{5, 6}
共有 7 種可能組合。
$$\therefore P = \frac{7}{15}$$

分佈域 Range = 472 −136 = 336
四分位數間距 IQR = m −163
$$\begin{align*}
336 &= 3\times(m -163)\\
112 &= m -163\\
m &= 275
\end{align*}$$
\frac{5 +5 +5 +6 +9 +9 +11 +13 +m +n}{10} &= 7\\
63 +m +n &= 70\\
m +n &=7
\end{align*}$$
因此 m 和 n 的值只有以下可能
{1, 6}
{2, 5}
{3, 4}
I)
用計數機計算以上三種情況的標準差。
Calculate the standard deviations for all 3 possible cases with a calculator.
結果分別是 3.32, 3.19, 3.13。因此選項 I 正確。
II)
考慮以上三種情況,眾數都是 5。
The mode is 5 for all 3 possible cases.
因此選項 II 正確。
III)
計算以上三種情況的中位數
Calculate the median for all 3 possible cases.
結果分別是 6, 5.5, 5.5。因此選項 III 正確。
& u^\color{red}{2} & v^3 & w^\color{red}{1} \\
& u^3 & v^\color{red}{1} & w^2 \\
& u^2 & v^3 & w^4 \\
\hline
\text{HCF}\ =\ & u^2 & v^1 & w^1\\
\end{eqnarray}$$
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇 #17 代數式的 HCF 及 LCM
&\text{AF000000000BC}_{16}\\
=&\color{green}{10 \times 16^{12} +15 \times 16^{11}} \color{blue}{+11 \times 16^1 + 12}\\
=&\color{green}{10 \times 16 \times 16^{11} +15 \times 16^{11}} \color{blue}{+188}\\
=&\color{green}{160 \times 16^{11} +15 \times 16^{11}} \color{blue}{+188}\\
=&\color{green}{175\times 16^{11}} \color{blue}{+188}
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{cases}
x = u -2\\
u^2 = 5u +x -7
\end{cases}$$ $$\begin{align*}
\therefore u^2 &= 5u +(u -2) -7\\
u^2 -6u +9 &= 0\\
(u -3)^2 &= 0\\
u &=3\\
\ \\
\log_2 y &= 3\\
y &= 2^3\\
y &=8
\end{align*}$$
y^3 -0 &= -16(\sqrt{x} -2)\\
y ^3 &= -16\sqrt{x} +32\\
\ \\
\text{當}\ x=36,\\
y^3 &= -16\sqrt{36} +32\\
y^3 &= -64\\
y &= -4
\end{align*}$$
相關文章:HKDSE 2018 數學科 Paper II Q33 題解
z &= (a -5)i +\frac{(a +2)i}{2 +i}\\[2pt] &= (a -5)i +\frac{(ai +2i)(2 -i)}{(2 +i)(2 -i)}\\[2pt] &= (a -5)i +\frac{2ai -ai^2 +4i -2i^2}{4 -i^2}\\[2pt] &= (a -5)i +\frac{2ai +a +4i +2}{4 +1}\ (\because i^2=-1)\\[2pt] &= (a -5)i +\frac{a +2 +(2a +4)i}{5}\\[2pt] &= \frac{a +2}{5} +(a -5)i + \frac{2a +4}{5}i
\end{align*}$$
∵ z 是實數 real number
$$\begin{align*}
(a -5)i + \frac{2a +4}{5}i &= 0\\
5a -25 + 2a +4 &= 0\\
7a -21 &= 0\\
a &= 3
\end{align*}$$ $$\begin{align*}
z &= \frac{a +2}{5}\\[2pt]
z &= \frac{3 +2}{5}\\
z &= 1
\end{align*}\\
\ \\
a -z = 3 -1 =2$$
先用以上公式求取通項。
Find the general term with the formula.
$$\begin{align*}
T(n) &=S(n) -S(n -1)\\
&=n(2n +3) -(n -1)(2(n -1) +3)\\
&=2n^2 +3n -(n -1)(2n +1)\\
&=2n^2 +3n -(2n^2 +n -2n -1)\\
&=2n^2 +3n -2n^2 +n +1\\
&= 4n +1
\end{align*}$$
I)
$$\begin{align*}
T(n) = 4n +1 &= 14\\
4n &= 13\\
n &= \frac{13}{4}
\end{align*}$$
由於 n 不是整數,因此選項 I 錯誤。
II)
已知通項 General Term 是 4n + 1,因此選項 II 正確。
III)
$$\begin{align*}
T(n) &= 4n +1\\
&=4n -4 +4 +1\\
&=4(n -1) +5\\
&= 5 +(n -1)4
\end{align*}$$
因為通項能以 ##a +(n -1)d## 表示,因此該數列為等差數列。
Since the general term can be expressed as ##a +(n -1)d##, the sequence is an arithmetic sequence.
因此選項 III 正確。
Tips: 若 T(n) 能以 an + b 的方式表示,該數列便是等差數列 A.S.。

透過聯立方程(Simultaneous Equations),可找到 P, Q 及 R 點坐標。
P 點:x +4y =13\\
2x -y=-1
\end{cases}\\[4pt] P=(1,3)
$$
x -2y =1\\
2x -y=-1
\end{cases}\\[4pt] Q=(-1,-1)
$$
x -2y =1\\
x +4y=13
\end{cases}\\[4pt] R=(5,2)
$$
然後把各點坐標代入 5x − 2y。
P: 5(1) −2(3) = −1Q: 5(−1) −2(−1) = −3
R: 5(5) −2(2) = 21
因此 5x − 2y 的最小值是 −3
$$\begin{align*}
\color{blue}{5x -2y} +c &= 22\\
\color{blue}{-3} +c &= 22\\
c &= 25
\end{align*}$$

$$\color{red}{\angle DCA }=\color{green}{ \angle TAD }= 55\deg \ (\angle\ in\ alt.\ segment\ \text{交錯弓形的圓周角})$$
在 BEDC,
在 △PCD,
\angle CPD + \color{blue}{\angle PDC} &= \angle BCD\\
29\deg + \color{blue}{\angle PDC} &= 55\deg +43\deg\\
\color{blue}{\angle PDC} &= 69\deg
\end{align*}$$ $$\begin{align*}
\color{blue}{\angle CBE} &=\color{blue}{ \angle PDC}\\
&= 69\deg
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
4u^2 -3u -1 &= 0\\
u =1\ \text{or}\ u &=-0.25
\end{align*}$$
當 ##\cos\theta = 1##,
\cos\theta &= 1\\
\theta &= 360\deg\ \ (\text{留意}\ \theta\neq 0\deg)
\end{align*}$$
當 ##\cos\theta = -0.25##,
\cos\theta &= -0.25\\
\theta &= (180\deg -75.5\deg)\ \text{or}\ (180\deg +75.5\deg)\\
\theta &= 104.5\deg\ \text{or}\ 255.5\deg
\end{align*}$$
所以共有3個根(roots)。

$$\begin{align*}
\tan 30\deg &= \frac{QS}{QP}\\
\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} &= \frac{1}{QP}\\
QP &= \sqrt{3}\\
\ \\
\sin 30\deg &= \frac{QS}{SP}\\
\frac{1}{2} &= \frac{1}{SP}\\[2pt]
SP &= 2\\
\ \\
\tan 45\deg &= \frac{QS}{QR}\\[2pt]
1 &= \frac{1}{QR}\\[2pt]
QR &= 1\\
\ \\
\sin 45\deg &= \frac{QS}{SR}\\[2pt]
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} &= \frac{1}{SR}\\[2pt]
SR &= \sqrt{2}
\end{align*}$$ $$
\begin{align*}
QR^2 + QP^2 &= PR^2\\
1^2 +(\sqrt{3})^2 &= PR^2\\
PR &= 2
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
\cos \angle PRS &= \frac{SR^2 +PR^2 -SP^2}{2(SR)(PR)}\\
&= \frac{(\sqrt{2})^2 +2^2 -2^2}{2(\sqrt{2})(2)}\\
&= \frac{2}{4\sqrt{2}}\\
&= \frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\\
&= \frac{1\times \sqrt{2}}{2\sqrt{2}\times \sqrt{2}}\\
&=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}
\end{align*}$$
I)
形心必定在三角形之內。
Centroid must lie inside the triangle.

因此選項 I 正確。
II)
對於鈍角三角形,垂心位於三角形之外。
For obtuse triangles, the orthocentres lie outside the triangle.

因此選項 II 正確。
III)
留意該三角形為等腰三角形。紅色線是三角形的角平分線及垂直平分線。因此 I 點及 J 點都必定在紅色線上。而 Q 點並不在紅色線上。
Note that the triangle is an isosceles triangle. The red line is the angle bisector and perpendicular bisector of the triangle. Thus, point I and point J must lie on the red line. But point Q does not.
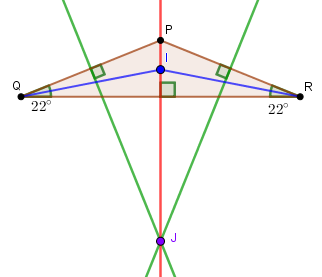
因此選項 III 錯誤。
經理站在一起的排列數目 = 8! × 2! = 80640
= 362880 − 80640 = 282240
P(\text{答對最少一題}) &= 1 -P(\text{答對零題})\\
&= 1- (1 -0.6)(1 -0.7)(1 -0.8)\\
&= 0.976
\end{align*}$$
$$\text{standard score 標準分 }z=\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}$$##\mu## = mean 平均值
##\sigma## = standard deviation 標準差
$$z=\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}$$##z## = standard score 標準分
##\mu## = mean 平均值
##\sigma## = standard deviation 標準差
I)
把各考試分數由小至大排列。
Arrange the scores in ascending order.
中位數 median ##=\frac{25 +26}{2} = 25.5##
因此選項 I 錯誤。
II)
用計數機得到
平均值 mean = 23.75, 標準差 standard deviation = 8.35
$$\begin{align*}
z &= \frac{x -\mu}{\sigma}\\
2 &= \frac{x -23.75}{8.35}\\
x &= 40.45
\end{align*}$$
所有分數都小於 40.45,因此選項 II 正確。
III)
標準差 standard deviation = 8.35,因此選項 III 正確。
方差 Variance = (標準差 Standard Deviation)²
在每個數據乘上相同的常數 k。
Standard Deviation 標準差為原來的 k倍。在每個數據加上相同的常數標準差並無改變。
Standard deviation does not change.
Standard Deviation 標準差 ##=\sqrt{16} \times 9 = 36##
分類: 計數機應用及歷屆試題



題解
Q35 個real part 計錯左, (a+2)/5, 唔係(a+4)/5
計到個a=3 直接代入 (a+2)/5 就計到 z=1
已修正! Thanks!
Q38 第二算式係△BEP
Corrected. Thanks!
questions thanks
can you send to my email plz