HKDSE 2020 Maths Paper II 題解
HKDSE 2020 Maths Paper II Answers and Solutions
香港中學文憑考試 2020 數學卷二答案+題解,括號內數字為答對百分率。
因版權關係,無法在網上刊登試題。請自行購買,或到公共圖書館借閱。
資料來源:香港考試及評核局─考試報告及試題專輯
&\ \frac{6x}{(3x^{-5})^{-2}}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{6x}{3^{-2} \times x^{10}}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{6x \times 3^2}{x^{10}}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{54}{x^9}
\end{align*}$$
a(a+b) &= 2(b-a)\\
a^2 + ab &= 2b -2a\\
ab -2b &= -a^2 -2a\\
b(a -2) &= -a^2 -2a\\
b &=\frac{-a^2 -2a}{a -2}\\[3pt] b &=\frac{a^2 +2a}{2 -a}
\end{align*}$$
&\ \frac{5}{4k +3} – \frac{2}{4k -3}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{5(4k -3) -2(4k+3)}{(4k +3)(4k -3)}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{20k -15 -8k -6}{16k^2 -9}\\[3pt] =&\ \frac{12k -21}{16k^2 -9}
\end{align*}$$
&\ (3a +2b)(4a -5b) -a(6a +4b)\\
=&\ \color{red}{(3a +2b)}(4a -5b) -2a\color{red}{(3a +2b)}\\
=&\ \color{red}{(3a +2b)}(4a -5b -2a)\\
=&\ (3a +2b)(2a -5b)
\end{align*}$$
&\ f(1 +\beta)\\
=&\ 3(1 +\beta)^2 -(1 +\beta) -2\\
=&\ 3(1 +2\beta +\beta^2) -1 -\beta -2\\
=&\ 3 +6\beta +3\beta^2 -3 -\beta\\
=&\ 3\beta^2 +5\beta\\[13pt] &\ f(1 -\beta)\\
=&\ 3(1 -\beta)^2 -(1 -\beta) -2\\
=&\ 3(1 -2\beta +\beta^2) -1 +\beta -2\\
=&\ 3 -6\beta +3\beta^2 -3 +\beta\\
=&\ 3\beta^2 -5\beta\\[13pt] &\ f(1 +\beta) -f(1 -\beta)\\
=&\ (3\beta^2 +5\beta) -(3\beta^2 -5\beta)\\
=&\ 3\beta^2 +5\beta -3\beta^2 +5\beta\\
=&\ 10\beta
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
g(-2) &= 0\\
a(-2)^3 +4a(-2)^2 -24 &=0\\
-8a +16a &= 24\\
8a &= 24\\
a &= 3
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ g(2)\\
=&\ 3(2)^3+4(3)(2)^2-24\\
=&\ 24 +48 -24\\
=&\ 48
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
\text{LHS} &= (x +h)(x +6)\\
&= x^2 +hx +6x +6h\\
&= x^2 \color{green}{+(h+6)}x \color{blue}{+6h}\\[12pt]
\text{RHS} &= (x +4)^2 +k\\
&= x^2 \color{green}{+8}x \color{blue}{+16 +k}
\end{align*}$$
Comparing the coefficient of like terms,
比較同類項係數,
$$\begin{cases}
h +6 = 8\\
6h = 16 +k
\end{cases}$$
Solving 解聯立方程,
$$h = 2, k = -4$$
方法二:
對於恆等式,x 是任何數值,該等式均成立。
Since it is an identity, the equality is always true regardless of values of x.
代 ##x = -6##,
$$\begin{align*}
(x +h) (x +6) &\equiv (x +4)^2 +k\\
(-6 +h) \color{red}{(-6 +6)} &= (-6 +4)^2 +k\\
\color{red}{0} &= 4+k\\
k &= -4
\end{align*}$$
x-intercept x截距 = ##-b##
y-intercept y截距 = ##\frac{-b}{a}##
slope 斜率 = ##\frac{-1}{a}##
從L1的 x截距及斜率的正負,可判斷 ##a \lt 0,b\gt0##
##L_2: bx +y +c = 0##
x-intercept x截距 = ##\frac{-c}{b}##
y-intercept y截距 = ##-c##
slope 斜率 = ##-b##
從L2的 y截距的正負,可判斷 ##c \lt 0##
I) 已判斷 ##c \lt 0##,所以選項 I 正確。
II) 比較它們的斜率 slope
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{-1}{a} &\gt -b\\
\frac{1}{a} &\lt b\\
1 &\gt ab\ \ (\because a\lt0)\\
ab &\lt 1
\end{align*}$$
∴選項 II 正確。
III) 比較它們的 y截距 y-intercept
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{-b}{a} &\lt -c\\
\frac{b}{a} &\gt c\\
b &\lt ac\ \ (\because a\lt0)\\
ac &\gt b
\end{align*}$$
∴選項 III 錯誤。
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇#3 圖像和係數的關係
Let the selling price and the cost be S and C respectively.
$$\begin{align*}
S\times(1 -x\%) &= C\\
\frac{S}{C} &= \frac{1}{1 -x\%}
\end{align*}$$
由於盈利率 = 25%,
Since percentage profit = 25%,
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{S-C}{C} = 25\%\\
\frac{S}{C} -\frac{C}{C} &= 0.25\\
\frac{S}{C} -1 &= 0.25\\
\frac{S}{C} &= 1.25\\
\frac{1}{1 -x\%} &= 1.25\ \big(\because \frac{S}{C}=\frac{1}{1 -x\%}\big)\\
1 -x\% &= \frac{1}{1.25}\\[3pt]
1-x\% &= 0.8\\
x\% &= 1-0.8\\
x\% &= 20\%
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
1\text{ km} &= 1000\text{ m}\\
1\text{ km} &= 100000\text{ cm}\\
1\text{ km}^2 &= 100000^2\text{ cm}^2
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
\Big( \frac{l_1}{l_2}\Big)^2 &= \frac{A_1}{A_2}\\
\Big( \frac{l_1}{l_2}\Big)^2 &= \frac{300\text{ cm}^2}{0.75\text{ km}^2}\\
\Big( \frac{l_1}{l_2}\Big)^2 &= \frac{300\text{ cm}^2}{0.75 \times 100000^2\text{ cm}^2}\\
\Big( \frac{l_1}{l_2}\Big)^2 &= \frac{1}{25000000}\\
\frac{l_1}{l_2} &= \frac{1}{5000}
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
w &=ku^3\sqrt{v}\\
8 &=k \times 2^3 \times \sqrt{4}\\
8 &= 16k\\
k &= \frac{1}{2}\\[12pt]
w &=\frac{1}{2} \times 4^3 \times \sqrt{9}\\
&= 96
\end{align*}$$
$$(n+1)^{\text{th}}\text{ term} = n^{\text{th}}\text{ term} + (2n +1)$$
$$\begin{array} {c|l|c} n & n^{\text{th}}\text{ term} & 2n+1 \\ \hline 1 & 3 & 3 \\ \hline 2 & 3+3=6 & 5 \\ \hline 3 & 6+5=11 & 7 \\ \hline 4 & 11+7=18 & 9 \\ \hline 5 & 18+9=27 & 11 \\ \hline 6 & 27+11=38 & 13 \\ \hline 7 & 38+13=\color{red}{51} & \end{array}$$
方法二: 觀察數列的模式 Observe the pattern
參考以下圖像,黑色數字為各圖案點子的數目,紅色數字為它們的差。從而得知每項之差每次增加2。
Referring to the figure below, the numbers in black are the numbers of dots of each pattern and the numbers in red are their differences. Thus, it can be determined that each difference increases by 2.

$$1^\text{st} \text{ term} = \ 3\\
2^\text{nd} \text{ term} = \ 3+3 = 6\\
3^\text{rd} \text{ term} = \ 6+5 = 11\\
4^\text{th} \text{ term} = 11+7 = 18\\
5^\text{th} \text{ term} = 18+9 = 27\\
6^\text{th} \text{ term} = 27+11= 38\\
7^\text{th} \text{ term} = 38+13 = \color{red}{51}$$
5 -4x &\lt 9 & \text{and}&\ & \frac{2x -3}{7} &\gt 1\\
-4x &\lt 9 -5 & \text{and}&\ & 2x -3 &\gt 7\\
x &\gt \frac{4}{-4} & \text{and}&\ & 2x &\gt 10\\
x &\gt -1 & \text{and}&\ & x &\gt 5\\[9pt] \therefore x\gt 5
\end{align*}$$

把圖形分割成一個長方形及一個梯形,要得到最大面積,就要把每條邊取最大值。 PT、QR 及 PQ 都是取最大值,即是
PT = 5.5 cm
QR = 10.5 cm
PQ = 6.5 cm
問題是 SR,如果取 3.5cm,就會令 PM 變短。但如果取 2.5cm,雖然 PM 長度增加,但卻令 MQ 的長度變短。
解決此問題最簡單的方法就是「逐個試」
取 SR = 3.5cm
$$\text{面積 }= \frac{(10.5+5.5) \times (6.5-3.5)}{2} + 10.5 \times 3.5 = 60.75$$
取 SR = 2.5cm
$$\text{面積 }= \frac{(10.5+5.5) \times (6.5-2.5)}{2} + 10.5 \times 2.5 = 58.25$$
較大者為 60.75,所以面積上限=60.75cm2
在四個選項中,只有選項 B 的上限是 60.75,足以判斷答案為 B。
$$\begin{align*}
2 \pi \color{red}{r(1+k\%)} \times \frac{\color{green}{\theta \times (1-60\%)}}{360\deg} &= 2 \pi r \times \frac{\theta}{360\deg}\\[3pt]
(1 +k\%) \times 0.4 &= 1\\[3pt]
1 +k\% &= \frac{1}{0.4}\\[3pt]
1 +k\% &= 2.5\\[3pt]
k\% &= 1.5\\
k\% &= 150\%
\end{align*}$$
\text{Volume of cone 圓錐體體積}=\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h##
=\pi r^2 h\\
\ \text{Volume of cone 圓錐體體積}\\
=\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h##
$$\begin{align*}
\pi (5a)^2 (7b) &= 525\\
\pi \times 175 a^2b &= 525\\
a^2b &= \frac{525}{175\pi}\\
a^2b&= \frac{3}{\pi}
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ \text{Volume of cone 圓錐體體積}\\
=&\ \frac{1}{3} \pi (7a)^2 (5b)\\[3pt]
=&\ \frac{1}{3} \pi \times 49a^2 \times 5b\\[3pt]
=&\ \frac{245 \pi}{3} \times a^2b\\[3pt]
=&\ \frac{245 \pi}{3} \times \frac{3}{\pi}\\[3pt]
=&\ 245\text{ cm}^3
\end{align*}$$
已知 ##OP:OQ:OR = 1:2:3##,參考下圖。

$$\begin{align*}
A_1:A_2:A_3 =& 1^2:2^2:3^2\\
=& 1:4:9
\end{align*}$$
PQTU\text{ Area}:QRST\text{ Area} &= (4 -1): (9-4)\\
&= 3:5
\end{align*}$$
&PQTU\text{ Area}:QRST\text{ Area}\\
=& (4 -1): (9-4)\\
=& 3:5
\end{align*}$$

$$\because \triangle AEG \sim \triangle ADB\\[4pt]
\begin{align*}
\therefore \frac{48}{48 +A_0} &= \Big(\frac{2k}{2k +5k}\Big)^2\\[2pt]
\frac{48}{48 +A_0} &= \frac{4}{49}\\
48 \times 49 &= 4(48 + A_0)\\
2352 &= 192 +4A_0\\
A_0 &= 540\text{ cm}^2
\end{align*}$$
由於 DB 是平行四邊形 DCBA 的對角線,
Since DB is a diagonal of parallelogram DCBA,
$$\therefore A_1 = 48 + 540 = 588\text{ cm}^2$$
Step 2) 求 BG:CD
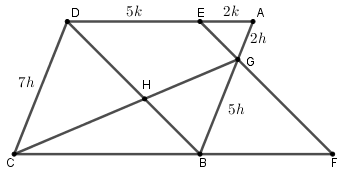
$$\begin{align*}
AG:GB &= AE:ED\\
&= 2:5\end{align*}$$
$$\because AB = CD\\
\therefore BG:CD = 5:7$$
Step 3) 求 ΔCDH 面積

留意 DCBG 是一個梯形,依照 《文憑試實戰篇 #6 破解在梯形內求面積的問題》 所述的方法,得到
$$A_2:A_3 = 7: 5$$
$$\because A_2 +A_3 = 588\\
\begin{align*}\therefore A_2 &= 588 \times \frac{7}{7+5}\\[3pt]
&=343\text{ cm}^2
\end{align*}$$
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇 #22 再談面積問題
加上平行線。Construct a parallel line.

$$\begin{align*}
u +(180\deg -w) +v &= 360\deg\\
u +v -w &= 180\deg
\end{align*}$$
I)
已知選項 II 必定正確。如果選項 I 正確,
Option II must be true. If option I is also true,
$$\begin{cases}
u -v +w = 0\deg\ …(1)\\
u +v -w = 180\deg\ …(2)
\end{cases}$$
(1)+(2),
$$\begin{align*}
2u &= 180\deg\\
u &= 90\deg
\end{align*}$$
但 u 並非必定等於 90°,因此選項 I 並非必為正確。
Since u=90° is not always true, option I is also not always true.
III)
已知選項 II 必定正確。如果選項 III 正確,
Option II must be true. If option III is also true,
$$\begin{cases}
u +v +w = 450\deg\ …(1)\\
u +v -w = 180\deg\ …(2)
\end{cases}$$
(1)−(2),
$$\begin{align*}
2w &= 270\deg\\
w &= 135\deg
\end{align*}$$
但 w 並非必定等於 135°,因此選項 III 並非必為正確。
Since w=135° is not always true, option III is also not always true.
下圖為該圖像的真實形狀。

留意∠ADC=∠CAD,即是 CA=CD。

$$\begin{align*}
\alpha =&\ 180\deg -40\deg -40\deg\\
=&\ \color{red}{100\deg}\\[12pt]
\beta =&\ 360\deg -\color{red}{100\deg} -\color{blue}{60\deg} -\color{green}{78\deg}\\
=&\ \color{orange}{122\deg}\\[12pt]
\theta =&\ (180\deg -\color{orange}{122\deg})\div 2\\
=&\ 29\deg
\end{align*}$$
 1) ΔEBC 佔整個長方形的一半。
1) ΔEBC 佔整個長方形的一半。2) ∠BEC = 90°,證明如下:
$$\begin{align*}
BE^2 +EC^2 &= 8^2 +15^2\\
&= 289\\[6pt] BC^2 &= 17^2\\
&= 289\\[10pt] \therefore BE^2 +EC^2 &= BC^2
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\ ABCD\text{ 面積}\\[2pt]
=&\ \triangle EBC \text{ 面積} \times 2\\[2pt]
=&\ \frac{8\times 15}{2} \times 2\\[3pt]
=&\ 120\text{ cm}^2
\end{align*}$$
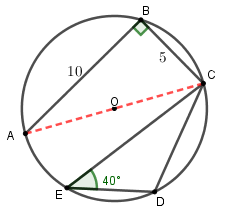
∵∠ABC=90°
∴ AC 是圓形的直徑
$$\begin{align*}
AC^2 &= 10^2 +25^2\\
AC &= \sqrt{125}
\end{align*}$$
連接 AD,得到
1) ∠CAD=40° (∠ in the same segment)
2) ∠ADC=90°

$$\text{In }\triangle ADC,\\
\begin{align*}
\sin 40\deg &= \frac{CD}{AC}\\[3pt]
\sin 40\deg &= \frac{CD}{\sqrt{125}}\\[3pt]
CD &= \sqrt{125}\times\sin 40\deg\\
&= 7.19\\
&\approx 7\text{ cm}
\end{align*}$$
 $$\begin{align*}
$$\begin{align*}\sin(90\deg -60\deg) &= \frac{x}{50}\\[3pt] x &= 50\sin 30\deg\\
&= 25\text{ km}
\end{align*}$$

只有從右至左把其變換還原,便能找到 P點坐標為 (-1,-1)。

然後用計算機或以下的方法,把 (-1,-1) 轉換成極坐標 Polar Coordinates

$$\begin{align*}
r &= \sqrt{1^2 +1^2}\\
&= \sqrt{2}
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
\tan \alpha &= \frac{1}{1}\\
\alpha &= 45\deg\\[8pt]
\theta &= 180\deg +45\deg\\
&= 225\deg
\end{align*}$$
$$\therefore P=(\sqrt{2},225\deg)$$
相關文章:文憑試實戰篇#2 Polar Coordinates 極坐標
Point A is a fixed point. The distance between Point P and Point A is a constant. Thus, its locus is a circle.

相關文章: 常見軌跡 Common Loci
Find the slopes of the straight lines.
$$\begin{align*}
kx +4y -2k &= 0\\
4y &= -kx +2k\\
y &= \frac{-k}{4}x + \frac{k}{2}\ …(1)\\[8pt]
\text{slope} &= \frac{-k}{4}
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
6x -9y +4 &= 0\\
-9y &= -6x -4\\
y &= \frac{-6}{-9}x -\frac{4}{-9}\\
y &= \frac{2}{3}x +\frac{4}{9}\\[8pt]
\text{slope} &= \frac{2}{3}
\end{align*}$$
由於它們互相垂直,因此斜率的積 =−1。
Since they are perpendicular, the product of the slopes =−1.
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{-k}{4} \times \frac{2}{3} &= -1\\
\frac{-2k}{12} &=-1\\
-2k &= -12\\
k &= 6
\end{align*}$$
從 (1), L1 的 y-截距為 ##\frac{k}{2}##。
From (1), the y-intercept of L1 is ##\frac{k}{2}##.
$$\begin{align*}
y\text{-intercept} &= \frac{k}{2}\\[3pt]
&=\frac{6}{2}\\[3pt]
&=3
\end{align*}$$
相關文章:兩直線互相垂直小貼士
$$\begin{align*}
C_1: 2x^2 +2y^2 +4x +8y -149 &= 0\\
x^2 +y^2 +2x +4y -74.5 &= 0
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
O_1 =& (-1,-2)\\
r_1 =& \sqrt{1^2 +2^2 +74.5}\\
=&\sqrt{79.5}\\
\approx&\ 8.92
\end{align*}
$$
$$\begin{align*}
C_2: x^2+y^2 -8x -20y -53 &= 0
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
O_2 =& (4,10)\\
r_2 =& \sqrt{4^2 +10^2 +53}\\
=&\sqrt{169}\\
=&13
\end{align*}$$
I) 把 C1 圓心代入 C2
$$\begin{align*}
\text{LHS} &= x^2+y^2 -8x -20y -53\\
&= (-1)^2 +(-2)^2 -8(-1) -20(-2) -53\\
&= 0
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 I 正確。
II)
r_1 &= \sqrt{79.5}\\
r_2 &= 13
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 II 錯誤。
III) 透過作圖來判斷。C1 的圓心在 C2 的圓周之上,而且 C1 的半徑比 C2 的半徑短,因此其圖像是這樣:

∴ 選項 III 正確。
*** Important ***
不可只用 (r1 + r2) > (兩圓心之距離) 來判斷它們相交於兩點。參考下圖,當 ##r_1 \gt 26 ## 時,兩個圓形並不相交。

兩個圓形相交於兩點的正確條件是:
$$\lvert r_1 -r_2 \rvert \lt \text{兩圓心之距離} \lt (r_1+r_2)$$
相關文章:兩圓形的交點數目
&\ \text{P}(>35)\\
=&\ \text{P}(5 \times 9) + \text{P}(7 \times 9)\\
=&\ \frac{1}{4}\times\frac{1}{3}\times 2 + \frac{1}{4}\times\frac{1}{3}\times 2\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{1}{3}
\end{align*}$$

從棒形圖得到:
Q_1 &= (5 +5) \div 2 = 5\\
Q_3 &= (6 +6) \div 2 = 6\\[12pt] \text{IQR} &= 6 -5 = 1
\end{align*}$$
II) mean 平均數 = 8
由於不確定 m 與 n 的值,所以無法計算平均值。因此選項 II 並非必為正確,並且可排除答案 B 及 D。
III) mode 眾數 = 8
如果 ##m=n=3##,眾數 mode = 3。因此選項 II 並非必為正確,並且可排除答案 C 及 D。
到此已可確定答案是 A。
I) median 中位數 = 8
這選項相對困難。
1) 如果只考慮已知的 7 個數據,其中位數是 8。假設 m 及 n 都大於 8。如 m=10, n= 11。
3 3 8 8 8 10 10 11 12
中位數 median = 8
2) 同樣,假設 m 及 n 都小於 8,如 m=4, n= 5
3 3 4 5 8 8 8 10 12
中位數 median = 8
兩個情況下中位數 median 仍是 8,所以選項 I 必為正確。
相關文章: 如何把中位數移動至指定數值
=& 11 \times 16^{15} + 3 \times 16^1\\
=& 11 \times \big(2^4\big)^{15} + 48\\
=& 11 \times 2^{60} + 48
\end{align*}$$
方法二:借助計數機
##\text{B000000000000030}_{16} = 11 \times 16^{15} + 3 \times 16^1\\[4pt]
11 \times 16^{15} = \color{red}{1.2682 \times 10^{19}}\\
3 \times 16^1 = \color{blue}{48}##
A)
##10 \times 2^{60} = 1.1529 \times 10^{19} \neq 1.2682 \times 10^{19}##
因此選項 A 錯誤。
B)
##11 \times 2^{60} = \color{red}{1.2682 \times 10^{19}}\\[2pt]
48 = \color{blue}{48}##
因此選項 B 為正確答案。
C)
##10 \times 2^{64} = 1.8447 \times 10^{20} \neq 1.2682 \times 10^{19}##
因此選項 C 錯誤。
D)
##11 \times 2^{64} = 2.0291\times 10^{20} \neq 1.2682 \times 10^{19}##
因此選項 D 錯誤。
$$\begin{align*}
(\log_\pi x)^2 -10\log_\pi x +24 &= \log_\pi x\\
u^2 -10u +24 &= u\\
u^2 -11u +24 &= 0\\
u &=8\ \ \text{or}\ \ 3\\
\log_\pi x &=8\ \ \text{or}\ \ 3\\
x &= \pi^8\ \ \text{or}\ \ \pi^3\\[10pt]
\alpha \beta &= \pi^8 \times \pi^3\\
&= \pi^{11}
\end{align*}$$
相關文章: 解對數方程 Solving Logarithm Equations

I 和 II) 很明顯這兩個選項都是正確。
III) a 與 b 是倒數關係 (reciprocal)。
i.e. ## a =\frac{1}{b}##
$$\begin{align*}
&\ a \times b\\
=&\ \frac{1}{b} \times b\\
=&\ 1
\end{align*}$$
因此選項 III 正確。
$$\begin{align*}
\sqrt{y} &= \frac{1 -0}{0 -(-4)}x^3 +1\\[3pt] \sqrt{y} &= \frac{1}{4}x^3 +1
\end{align*}$$
When x = 2,
\sqrt{y} &= \frac{1}{4}(2)^3 +1\\[3pt] \sqrt{y} &= 3\\
(\sqrt{y})^2 &= 3^2\\
y &= 9
\end{align*}$$
相關文章: 文憑試實戰篇 #16 對數(log)與直線圖像
&\ \log a -\log a^{-3}\\
=&\ \log a +3\log a\\
=&\ 4\log a\\[10pt] &\ \log a^5 -\log a\\
=&\ 5\log a -\log a\\
=&\ 4\log a\\[10pt] \end{align*}$$
##\because \log a -\log a^{-3} = \log a^5 -\log a\\
\therefore \text{It is an arithmetic sequence.}##
II)
&\ (9 -5a) -(8 -4a)\\
=&\ 9 -5a -8 +4a\\
=&\ 1 -a\\[10pt] &\ (10 -6a) -(9 -5a)\\
=&\ 10 -6a -9 +5a\\
=&\ 1 -a\\[10pt] \end{align*}$$
##\because (9 -5a) -(8 -4a) = (10 -6a) -(9 -5a)\\
\therefore \text{It is an arithmetic sequence.}##
III)
&\ \cos 90\deg -\cos(90 -a)\deg\\
=&\ 0 -\sin a\deg\\
=&\ -\sin a\deg\\[10pt] &\ \cos (90 +a)\deg -\cos 90\deg\\
=&-\sin a\deg – 0\\
=&-\sin a\deg
\end{align*}$$
##\because \cos 90\deg -\cos(90 -a)\deg = \cos (90 +a)\deg -\cos 90\deg\\
\therefore \text{It is an arithmetic sequence.}##
$$2x +y +3=0\\
x\text{-intercept} = -1.5, y\text{-intercept} = -3\\[12pt]
x +y +1 =0\\
x\text{-intercept} = -1, y\text{-intercept} = -1$$
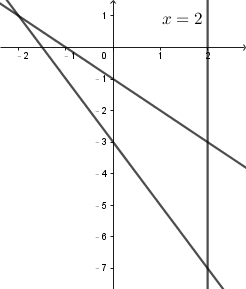
運用代數技巧,找到以下各點坐標。

然後求 ##4x+3y## 的最小值。
$$(0,-1):4(0)+3(-1)=-3\\
(0,-3):4(0)+3(-3)=-9\\
(2,-3):4(2)+3(-3)=-1\\
(2,-7):4(2)+3(-7)=\color{red}{-13}$$
已知 ##4x +3y +k## 的最小值是 24。
$$\begin{align*}
4(2)+3(-7)+k &= 24\\
-13 +k &=24\\
k &= 37
\end{align*}$$
z_1 &= \frac{2 +ki}{1 +ki}\\[2pt] &=\frac{(2 +ki)(1 -i)}{(1 +i)(1 -i)}\\[2pt] &-\frac{2 -2i +ki -ki^2}{1 -i^2}\\[2pt] &=\frac{2 +k -2i +ki}{1+1}\\[2pt] &=\frac{2 +k}{2} + \frac{k -2}{2}i
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
z_2 &= \frac{k +5i}{2 -i}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{(k +5i)(2 +i)}{(2 -i)(2+i)}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{2k +ki +10i +5i^2}{4 -i^2}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{2k -5 +ki +10i}{4 +1}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{2k -5}{5} +\frac{k +10}{5}i
\end{align*}$$
∵ 它們虛部相等。
Their imaginary parts are equal.
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{k -2}{2} &= \frac{k+10}{5}\\[2pt]
5k -10 &= 2k +20\\
3k &= 30\\
k &= 10
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&z_1 -z_2\\[2pt]
=&\ \Big(\frac{2+10}{2} +\frac{10 -2}{2}i\Big) -\Big(\frac{20 -5}{5} + \frac{10 +10}{5}i\Big)\\[2pt]
=&\ (6 +4i) -(3 +4i)\\
=&\ 6 +4i -3 -4i\\
=&\ 3
\end{align*}$$
BP and DP can be found by Pythagoras' Theorem.
$$\begin{align*}
BP^2 &= AP^2 +AB^2\\
BP^2 &= 9^2 +12^2\\
BP &= 15\\[12pt]
DP^2 &= EP^2 +ED^2\\
DP^2 &= 5^2 + 12^2\\
DP &= 13
\end{align*}$$
已知 ΔBDP 的三條邊長。

求它的面積,可用希羅公式 Heron's Formula
$$\begin{align*}
\text{Let }s &=\frac{2k+13+15}{2}\\[2pt]
&=\frac{2k+28}{2}\\[2pt]
&= k +14
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
&\text{Area 面積}\\
=& \sqrt{s(s -a)(s -b)(s -c)}\\
=& \sqrt{(k +14)(k +14 -13)(k +14 -15)(k+14 -2k)}\\
=& \sqrt{(k +14)(k +1)(k -1)(14 -k)}\\
=& \sqrt{\color{red}{(k +1)(k -1)} \color{blue}{(14 -k)(14 +k)}}\\
=& \sqrt{\color{red}{(k^2 -1)} \color{blue}{(196 -k^2)}}\ \text{cm}^2
\end{align*}$$

Step 1) 在大圓形中運用交錯弓形的圓周角 ∠ in alt. segment,可找到下圖中兩隻藍色的角。
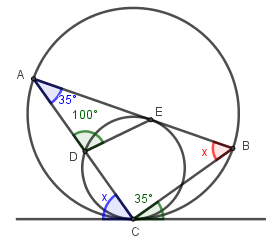
Step 2) 求下圖中兩隻紫色的角。

$$\begin{align*}
\angle AED &= 180\deg -35\deg -100\deg\\
&= 45\deg\\[8pt]
\angle CDE &= 180\deg -100\deg\\
&=80\deg
\end{align*}$$
Ste心 3) 連接 CE,在小圓形中運用交錯弓形的圓周角 ∠ in alt. segment,可找到下圖中兩隻綠色的角。
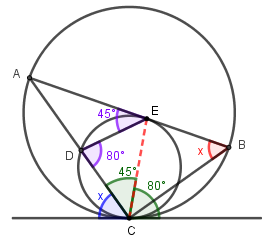
Step 4) 在 C 點,
$$\begin{align*}
x &= 180\deg -45\deg -80\deg\\
&= 55\deg
\end{align*}$$
Plot the two lines from their intercepts.

參考下圖,由於內心 In-centre 必定在三角形之內,所以 a > 31。而且內心在 x-軸上。

方法一: 從角平方線 Angle Bisector 入手。
Step 1) 求圖中 θ 的值。

$$\begin{align*}
\because \text{slope 斜率} &=\frac{4}{3}\\[2pt]
\therefore \tan \alpha &= \frac{4}{3}\\
\alpha &= 53.13\deg\\[10pt]
\theta &= 90\deg -53.13\deg\\
&= 36.87\deg
\end{align*}$$
Step 2) 留意下圖中的三角形

$$\begin{align*}
\tan \frac{\theta}{2} &= \frac{a -31}{\frac{4}{3}a-8}\\[3pt]
\tan \frac{36.87\deg}{2} &= \frac{a -31}{\frac{4}{3}a-8}\\[3pt]
0.3333 &= \frac{a -31}{\frac{4}{3}a-8}\\[3pt]
0.4444a -2.6664 &= a -31\\
28.3336 &= 0.5556a\\
a &=50.996\\
a &\approx 51
\end{align*}$$
方法二: 從內切圓 Inscribed Circle 入手。

$$\begin{align*}
\tan \alpha &= \frac{4}{3}\ \text{(From the slope)}\\[3pt]
\sin \alpha &= \frac{4}{5}\ \text{(By Calculator)}\\[3pt]
\frac{a -31}{31 -6} &= \frac{4}{5}\\[3pt]
5a -155 &= 100\\
5a &= 255\\
a &= 51
\end{align*}$$
x^2 +y^2 -6x +cy -7 =0\ …(1)\\
x -y +9 =0\ …(2)
\end{cases}$$
從 (2), ##y = x +9\ …(3)##
把 (3) 代入 (1),
$$\begin{align*}
x^2 +(x+9)^2 -6x +c(x +9) -7 &=0\\
x^2 +x^2 +18x +81 -6x +cx +9c -7 &=0\\
2x^2 +12x +cx +74 +9c &=0
\end{align*}$$
$$\begin{align*}
\Delta &\ge 0\\
(12+c)^2 -4(2)(74+9c) &\ge 0\\
144 +24c +c^2 -592 -72c &\ge 0\\
c^2 -48c -448 &\ge 0\\
c \le -8 \ \ \text{or}\ \ c&\ge 56
\end{align*}$$
下圖顯示當 c 的數值改變時,該圓形會怎樣變化。

相關文章: 文憑試實戰篇 #11 圓形方程進階答題技巧

下圖中藍色線的地方就是可放置男生的地方。可放置男生的地方有6處,而男生的數目亦是 6,因此共有 ##P_6^6## 種排列方式。

$$\begin{align*}
&\text{排列方式的總數}\\
=&\ 5! \times P_6^6\\
=&\ 86400
\end{align*}$$
&\ \text{P(最多3本中文書})\\[2pt] =&\ \text{P(0本中文書)}+\text{P(1本中文書)}+\text{P(2本中文書)}+\text{P(3本中文書)}\\[2pt] =&\ 1 -\text{P(4本中文書)} -\text{P(5本中文書)}\\[2pt] =&\ 1 -\frac{C^8_4 \times C^7_1}{C^{15}_5} -\frac{C^8_5}{C^{15}_5}\\[2pt] =&\ 1 -\frac{490}{3003} -\frac{56}{3003}\\[2pt] =&\ \frac{9}{11}
\end{align*}$$
$$\text{standard score 標準分 }z=\frac{x -\mu}{\sigma}$$##\mu## = mean 平均值
##\sigma## = standard deviation 標準差
$$z=\frac{x -\mu}{\sigma}$$##z## = standard score 標準分
##\mu## = mean 平均值
##\sigma## = standard deviation 標準差
兩者分數相差 30,設他們的分數分別為 (x+30) 及 x。
The difference of their marks is 30. Let their marks be (x+30) and x respectively.
設 μ and σ 分別為平均值及標準差。
Let μ and σ be the mean and standard deviation respectively.
∵ 標準分 Standard Scores 相差 6
$$\begin{align*}
\frac{(30 +x) -\mu}{\sigma} -\frac{x -\mu}{\sigma} &= 6\\
\frac{30 +x -\mu -x +\mu}{\sigma} &=6\\
\frac{30}{\sigma} &=6\\[2pt]
\sigma &= 5
\end{align*}$$
在每個數據加上共同的常數,標準差及方差並無改變。
Adding a common constant to each datum,The standard deviation and variance remain unchanged.
把每個數據都減去 20a,方差並無改變。
Subtracting 20a from each datum, the variance remains unchanged.
數據組變成: 3, 5, 9 ,11, 15,17
求它們的方差 Variance,先用計數機求它們的標準差 Standard Deviation,得到 5。
\text{Variance 方差} &= \text{(Standard Deviation 標準差)}^2\\
&= 5^2\\
&=25
\end{align*}$$
&\text{Variance 方差}\\
=&\text{(Standard Deviation 標準差)}^2\\
=& 5^2\\
=& 25
\end{align*}$$
分類: 計數機應用及歷屆試題



第40題可用相似三角形:
10/8 = (31-6)/r, 其中r是內接圓的半徑
可得 r=20, a=31+20=51
多譏你無私、充滿耐心的分享
Q38的圖片數值打錯了.
PD和PB的數值倒轉了.
已更正。Thanks!
十分有用,好人一生平安!
十分有幫助,簡單清晰,好人一生平安!